Normalisation/Scaling#
Normalisation and scaling are the process of scaling your data to some predetermined range. It is often between 0 and 1, but can be according to a model. Normalisation and scaling are often used when comparing different types of data in routines such as cluster analysis.
The options are:
Interval [0 1] - This simply stretches the data values between 0 and 1.
Mean: zero, Standard deviation: unity - This sets the mean of the dataset to 0, and the standard deviation of the dataset to +/- 1
Median: zero, Median absolute deviation: unity - This sets the median of the dataset to 0, and the median absolute deviation of the dataset to +/- 1
8-bit histogram equalisation [0 255] - this seeks to distribute the data equally across 255 values.
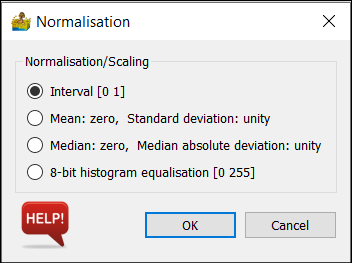
Normalisation options.#


